Table of Contents
Fertility Preservation for Cancer Patients: Expert Guide
Cancer is a challenging and life-altering disease that affects millions of people worldwide. For cancer patients, the focus is often on defeating the illness and regaining their health. However, cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy can have significant impacts on fertility.

Many cancer patients, especially those of reproductive age, are concerned about their ability to have children after cancer treatment. In recent years, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has emerged as a promising option for fertility preservation in cancer patients.
1. Introduction
In Vitro Fertilization, commonly known as IVF, is a medical procedure in which an egg is fertilized with sperm outside the body and then implanted into the uterus to establish a pregnancy. IVF has revolutionized the field of assisted reproductive technology and has offered hope to many individuals and couples struggling with infertility. Now, it also provides an opportunity for cancer patients to preserve their fertility before undergoing cancer treatments that may impair their reproductive capabilities.

Fertility preservation for cancer patients has gained significant attention in recent years, as advances in cancer treatment have led to improved survival rates. Many young adults diagnosed with cancer are now eager to preserve their ability to have biological children after their treatment is complete.
Let’s explore the importance of fertility preservation for cancer patients and how IVF can offer a ray of hope in such challenging circumstances.
2. Understanding Cancer and Fertility
Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells. However, these treatments can also affect healthy cells, including reproductive cells. In women, chemotherapy can damage the eggs and reduce ovarian reserve, leading to diminished fertility or premature menopause. Similarly, in men, these treatments can negatively impact sperm production and quality.

The loss of fertility during cancer treatment can have profound emotional consequences for patients. The fear of losing the ability to have biological children can add to the already overwhelming emotional burden of fighting cancer. Thus, fertility preservation becomes crucial for cancer patients who wish to build families in the future.
3. Options for Fertility Preservation for cancer patients
There are several options for fertility preservation for cancer patients. The choice of the method depends on factors such as age, gender, cancer type, and treatment plan. The most common methods include:
Egg Freezing:

Egg freezing, also known as oocyte cryopreservation, involves retrieving a woman’s eggs, freezing them, and storing them for later use. This option is suitable for women who do not have a partner or do not wish to use sperm from a partner in the future.
Sperm Freezing:
Sperm freezing is a straightforward and effective method for male cancer patients. Sperm samples are collected and frozen for later use in assisted reproductive techniques, including IVF.
Embryo Freezing:
For couples, embryo freezing is a viable option. It involves fertilizing retrieved eggs with sperm in the laboratory to create embryos, which are then frozen and stored for future implantation.
4. The IVF Process
IVF is the most commonly used fertility treatment and has helped millions of couples worldwide overcome infertility. For cancer patients seeking fertility preservation, the IVF process typically involves the following steps:
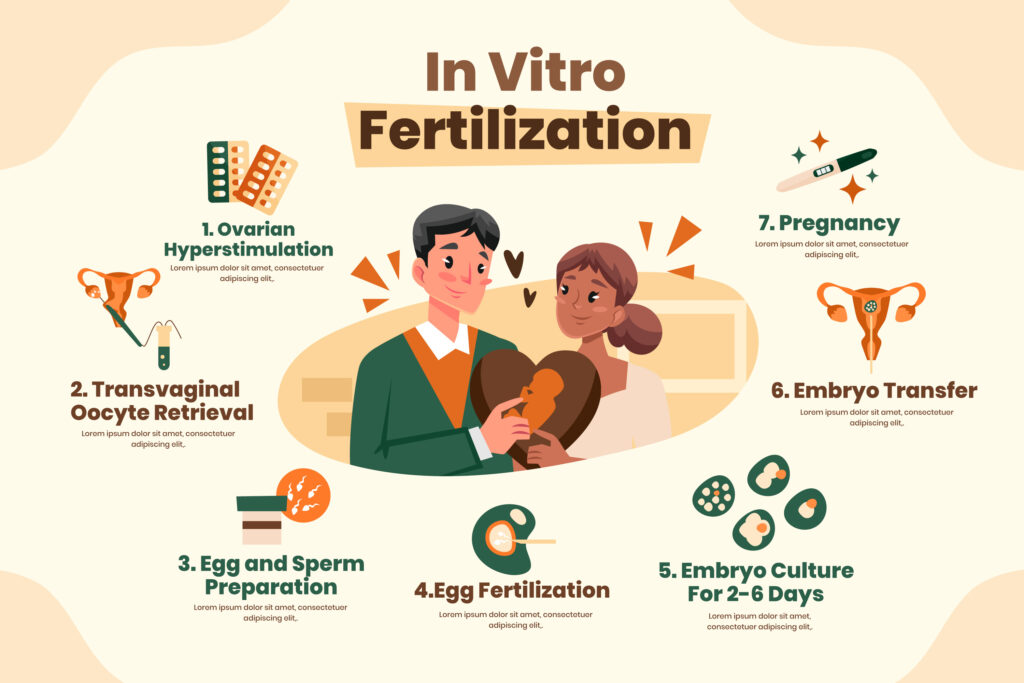
Ovarian Stimulation:
Before egg retrieval, the woman undergoes hormonal stimulation to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
Egg Retrieval:
Mature eggs are retrieved from the ovaries through a minor surgical procedure. The eggs are then prepared for fertilization.
Fertilization and Embryo Development:
The retrieved eggs are fertilized with sperm in the laboratory, and the resulting embryos are monitored for development.
–
Embryo Transfer:
In the final step, one or more healthy embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus with the hope of achieving a successful pregnancy.
5. Success Rate of IVF in Cancer Patients

The success rate of IVF in cancer patients depends on various factors, including the patient’s age, the quality of eggs or sperm, and the overall health of the patient. In some cases, cancer treatments can affect the success rates of IVF. However, advancements in reproductive technology and tailored treatment plans have led to improved outcomes.
6. Risks and Considerations
As with any medical procedure, IVF comes with certain risks and considerations. Physical risks may include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) and multiple pregnancies. It is essential for cancer patients to discuss these risks with their healthcare providers before making a decision.
On the emotional front, the process of fertility preservation and IVF can be emotionally taxing, especially when coupled with the emotional strain of battling cancer. Counseling and emotional support play a vital role in helping patients navigate this journey successfully.
8. Ethical and Legal Aspects
Fertility preservation for cancer patients raises ethical concerns, including the welfare of potential offspring and the use of assisted reproductive technology in the face of life-threatening illnesses. It is essential for medical professionals and patients to consider these ethical aspects while making decisions about fertility preservation.

Moreover, there are legal rights and protections in place for cancer patients seeking fertility preservation. Understanding these rights can empower patients to make informed choices about their future family-building options.
9. Future Directions and Advancements
The field of fertility preservation and IVF is continually evolving with ongoing research and innovations. New technologies and approaches are being developed to improve the effectiveness of fertility preservation for cancer patients. As science progresses, the prospects for preserving fertility in the face of cancer will only become more promising.
10. Conclusion
Fertility preservation for cancer patients through IVF offers hope to those facing the possibility of infertility due to cancer treatments. By safeguarding their reproductive potential before undergoing chemotherapy or radiation, cancer patients can retain the dream of building a family in the future. The emotional and psychological benefits of preserving fertility are immeasurable, providing patients with the strength and motivation to fight cancer with even greater determination.
With advancements in medical technology and a growing understanding of the emotional impact of cancer treatment, the future looks bright for cancer patients seeking fertility preservation. Through IVF and other fertility preservation options, cancer patients can take control of their reproductive future and embrace the possibility of a fulfilling family life beyond cancer.
FAQs
Is IVF suitable for all cancer patients?
IVF may not be suitable for every cancer patient. The eligibility for IVF and other fertility preservation options depends on various factors, such as the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient's overall health. It is essential for patients to discuss their specific case with a fertility specialist.
Does cancer treatment affect the success of IVF?
Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy can impact fertility and, in turn, affect the success of IVF. However, advancements in reproductive technology and personalized treatment plans have improved IVF success rates even for cancer patients. .
Are there any long-term health risks associated with IVF?
IVF is generally considered safe, but like any medical procedure, it comes with certain risks. Potential physical risks include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) and multiple pregnancies. Patients should thoroughly discuss these risks with their healthcare providers. d
Can fertility preservation options be used after cancer treatment?
In some cases, fertility preservation options may still be available after cancer treatment. However, the success rates and options may vary depending on the individual's circumstances. It is essential to explore fertility preservation before starting cancer treatment whenever possible.
Is fertility preservation covered by insurance?
Fertility preservation may or may not be covered by insurance, depending on the policy and location. Some insurance plans offer coverage for fertility preservation in cancer patients, but it is essential to check with the insurance provider before.

