Table of Contents
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Comprehensive Overview
1. Introduction to PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, often abbreviated as PCOS, is one of the most common endocrine disorders affecting women of reproductive age. With an alarming rise in the number of cases, understanding PCOS becomes imperative, not just for those who suffer from it but also for everyone aiming to be aware of women’s health issues. This article will elucidate what PCOS is, delve into the causes and symptoms, and highlight potential treatment avenues, emphasizing bilateral polycystic ovaries and pcod problems.
Must Read: Exploring Female Infertility Treatment in India
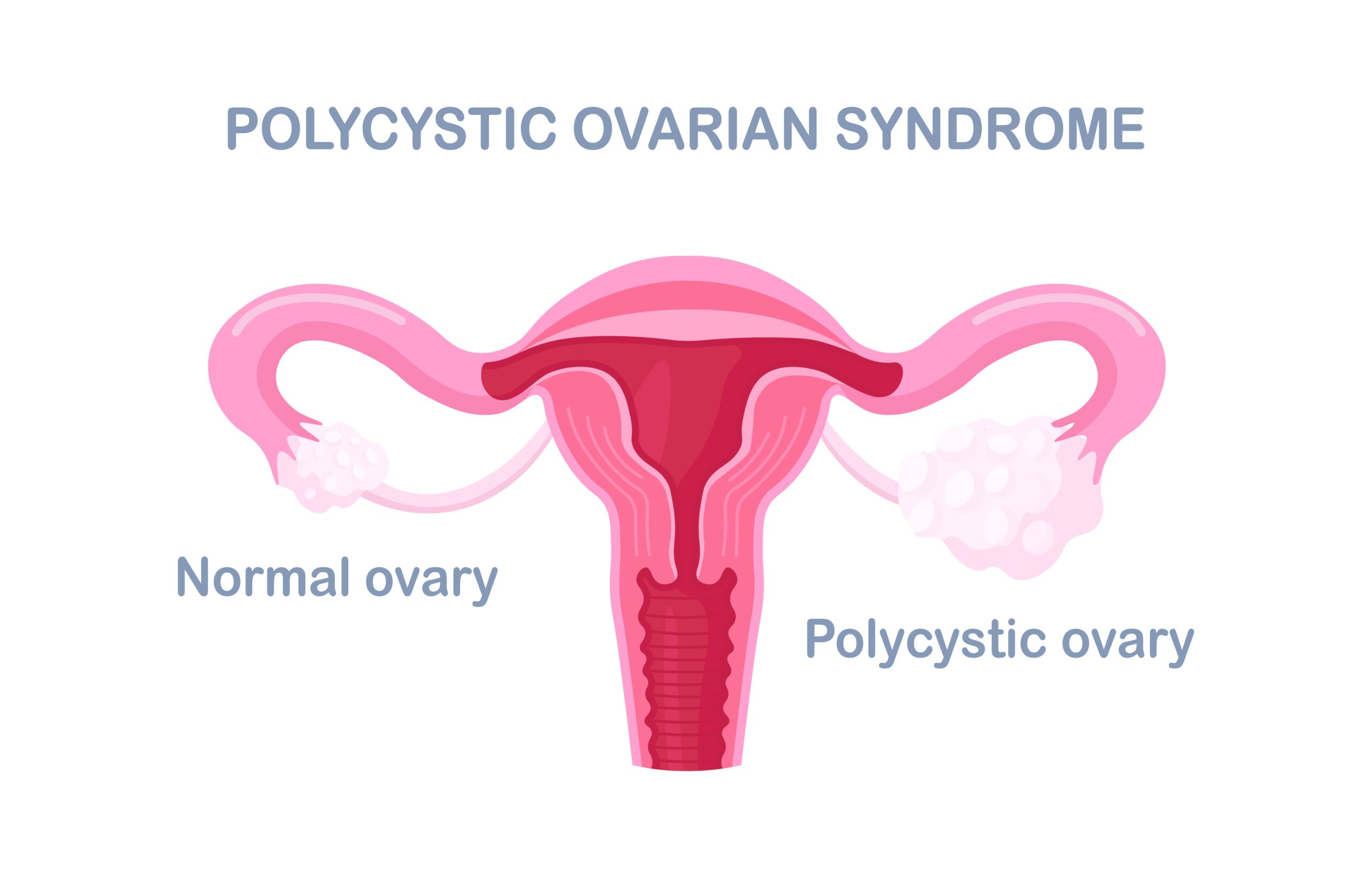
2. Understanding PCOD and Its Problems
PCOD vs. PCOS: At the outset, it’s vital to differentiate between PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) and PCOS. While both are related to ovarian anomalies, they differ slightly in terms of their causes and manifestation. PCOD is considered a milder version of PCOS. The former often results in enlarged ovaries with small cystic structures, while the latter is a more complex metabolic disorder affecting multiple body systems.
PCOD Problems: Those grappling with PCOD face several challenges, such as irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and hormonal imbalances. Over time, if not managed or treated, PCOD can escalate into PCOS, bringing with it a host of other potential health concerns, including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular issues.
3. Causes Behind PCOS
While the precise cause behind PCOS remains somewhat elusive, various factors contribute to its onset:
- Genetics: Research indicates a strong familial link. Women with a family history of PCOS are more likely to develop it.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) in women can prevent the ovaries from producing hormones and making eggs normally.
- Insulin Resistance: Over 50% of women with PCOS suffer from insulin resistance, leading to an overproduction of insulin. This excess insulin might boost androgen production, causing difficulties with ovulation.
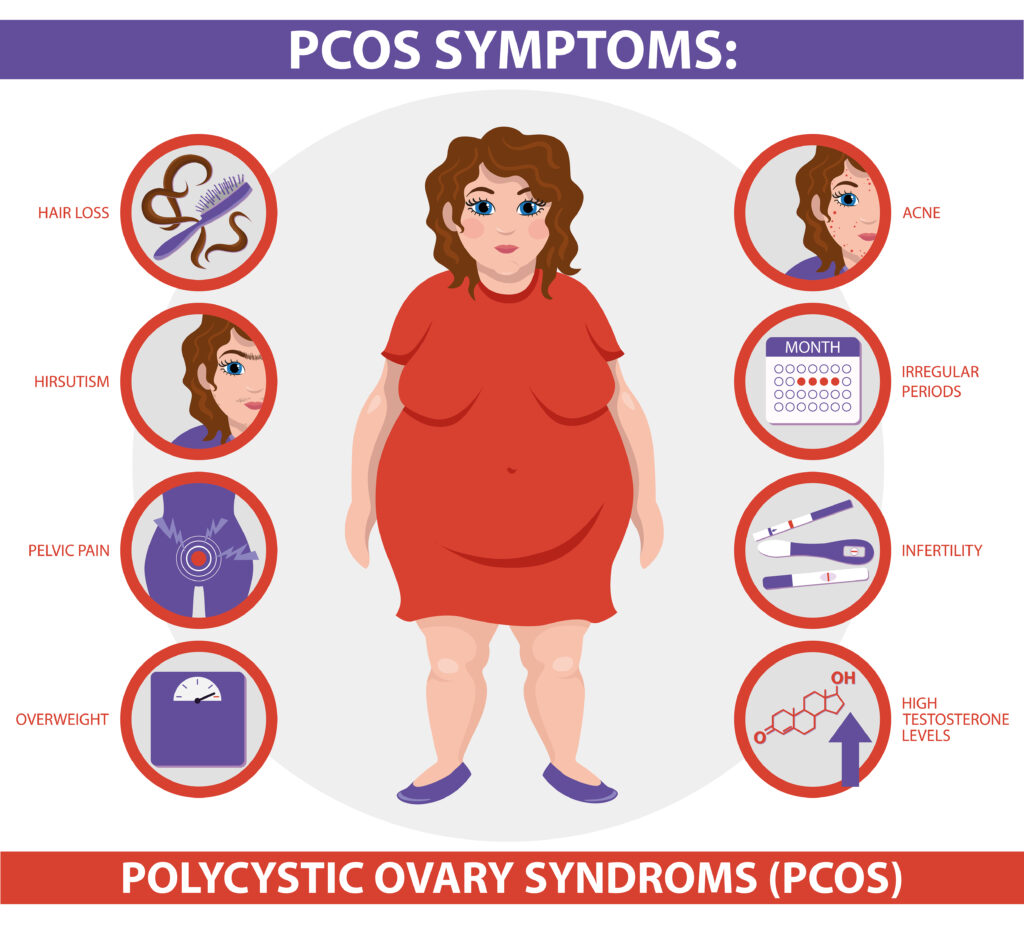
4. Identifying the Symptoms of PCOS
Detecting PCOS early can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Infrequent, irregular, or prolonged periods are among the most common signs.
- Heavy Bleeding: When periods do occur, they might be heavier than usual.
- Excess Androgen: Elevated levels can result in physical signs such as facial and body hair, severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
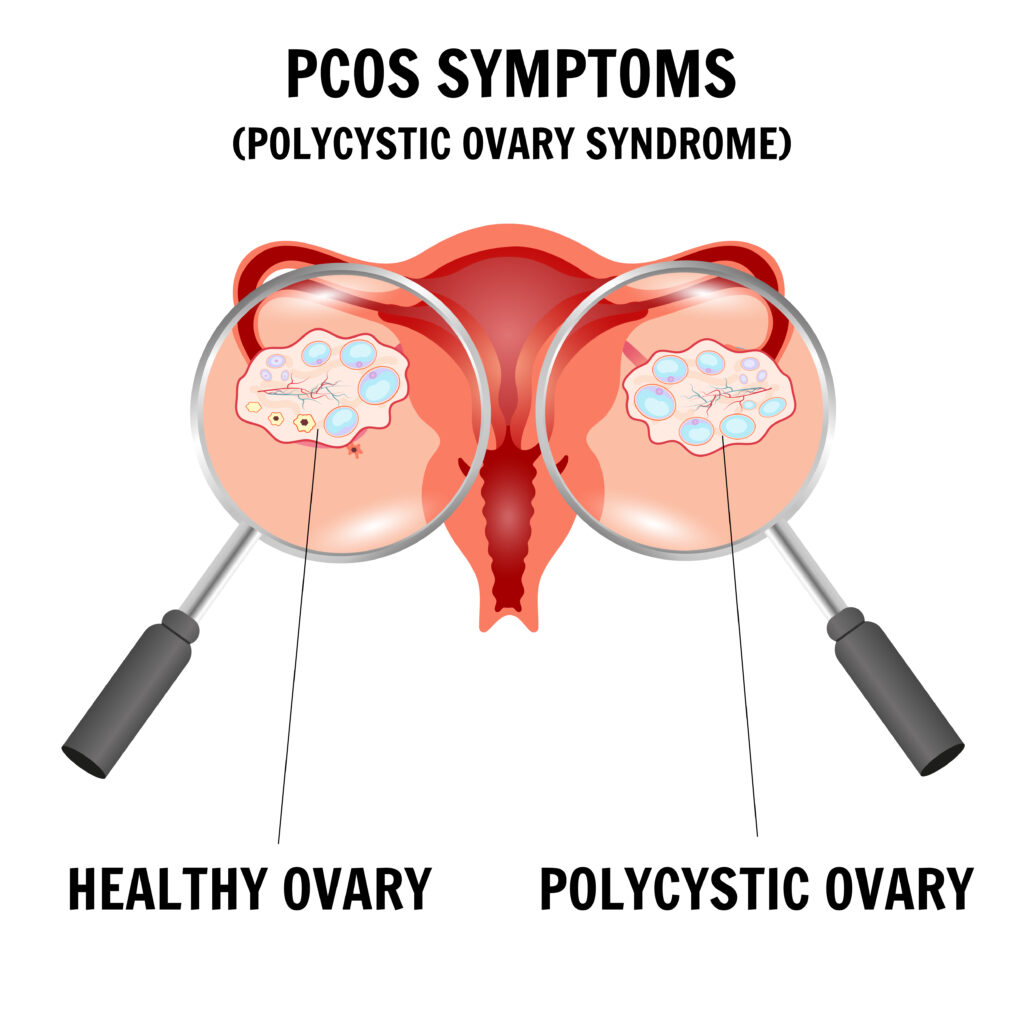
- Polycystic Ovaries: Ovaries might become enlarged and contain follicles that surround the eggs, leading to the ovaries failing to function regularly.
5. Bilateral PCOS and Its Implications
Bilateral Polycystic Ovaries: This term refers to the presence of multiple small cysts in both ovaries. It’s crucial to note that having bilateral polycystic ovaries doesn’t necessarily mean one has PCOS. Many women can have bilateral pcos without experiencing any symptoms or having PCOS.
Implications: While bilateral polycystic ovaries might not cause direct harm, it’s a significant marker for potential hormonal imbalances or future ovarian issues. These women need to be monitored closely for the onset of PCOS symptoms and other related conditions.
6. Efficient PCOS Treatment Options
Treating PCOS often involves addressing the individual’s predominant concerns like infertility, acne, or obesity. Some popular pcos treatment in india options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce PCOS symptoms and are often the first line of treatment.

- Medication: Birth control pills can regulate periods and reduce androgen levels. Metformin can improve insulin sensitivity, and Clomiphene can aid in ovulation.
- Surgery: In severe cases where other treatments don’t work, ovarian drilling, a procedure that involves making tiny punctures in the ovary with a small needle carrying an electric current, can be used to restore regular ovulation.
8. Conclusion
PCOS, while common, is a complex disorder that demands understanding and empathy. Early detection and appropriate treatment can go a long way in managing its symptoms and ensuring a better quality of life for those affected. Whether it’s the broader umbrella of PCOS or the specific realm of bilateral polycystic ovaries, awareness and proactive healthcare decisions can make all the difference.
It’s essential for everyone, especially young women, to be informed about PCOS. Not only to seek treatment if they suspect they have it but also to provide support to the countless women grappling with its challenges. The journey with PCOS is indeed tough, but with knowledge, medical advancement, and community support, it’s certainly not insurmountable.